

These isotopes are clearly matching with stable nuclides let’s understand how: You might have heard of isotopes, the two elements having the same atomic number but a different mass number. The above examples on parent nuclide and daughter nuclide also express the relationship between these two. Here, Iodine - 131 is the parent nucleus of Xenon - 131.Īu - 208, after undergoing the nuclear reaction, produces Hg - 208. Tellurium or Te-131 after undergoing β + decay forms a daughter nuclide called Iodine - 131. Here, Na-22 is the parent nuclide and Ne-22 is the daughter nuclide. It is a nuclide that decays into a daughter nuclide during the process of radioactive decay.įor example, Na-22 decays into Ne-22 after undergoing β + decay.
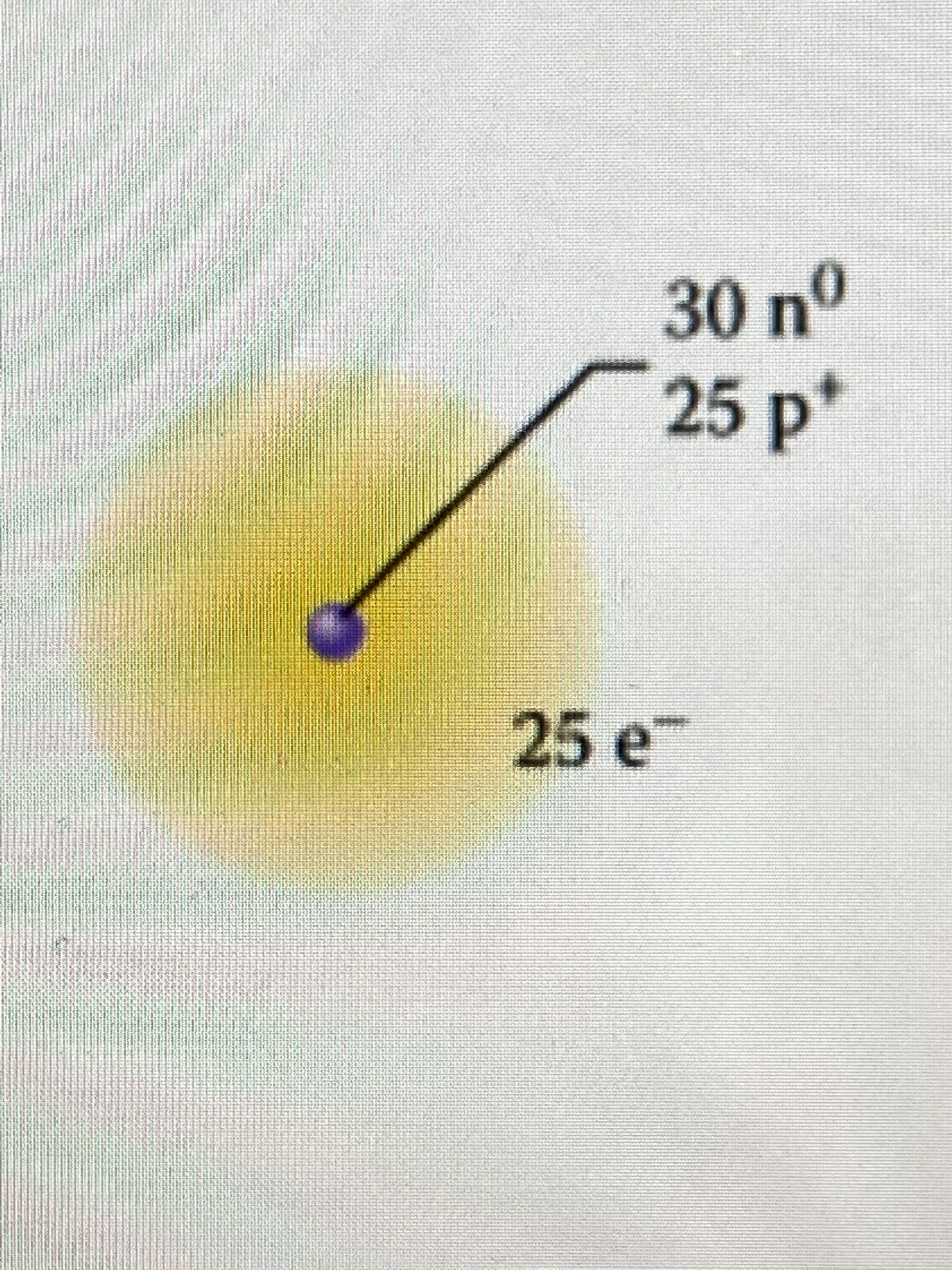
It is an isotope whose radioactive decay products are sure daughter nuclides. Now, we will understand the science behind the parent nuclide, daughter nuclide, stable nuclides with a graph in detail.Ī parent nuclide is a determinate nuclide. By using his newly devised invention, he also discovered more than 200 stable nuclides. In 1919, a British Physicist named Francis William Aston discovered the isotopes of the light elements (light elements are hydrogen, deuterium, helium (two isotopes), lithium, and trace amounts of beryllium) at the Cavendish Laboratory, using his new invention of the mass-spectrograph. Nuclides are linked with radioactive decay and they can either be stable or unstable species.Īround 1,700 nuclides are known, of which 300 are stable and the rest radioactive. Proton number is equal to Z = total number of protons = 3 Nucleon number A = total number of protons and neutrons = 7 The symbol for the “Li” element is given as We express nuclides in the form of A X Z, where “A” is the total number of protons and neutrons, “Z” denotes the number of protons, and the difference between A and Z is the number of neutrons. The term nuclide is not similar to an isotope, it is any member of a set of nuclides possessing the same atomic number but a different mass number.įor Example, Chlorine - 37 is the nucleus that comprises 17 protons and 20 neutrons, it is a different nuclide from the sodium - 23 nuclei having 11 protons and 12 neutrons, and chlorine - 35 nucleus of 17 protons and 18 neutrons.Įvery nuclide has a chemical element symbol (E) in addition to an atomic number (Z), i.e., the number of protons with inside the nucleus, and a mass number (A), i.e., the whole number of protons and neutrons within the nucleus. For considering it distinct, a nuclide must have an energy content enough for a measurable lifetime, i.e., more than 10 −10 seconds. On this page, you will learn about the nuclide, daughter nuclide, radioactive nuclide, parent nuclide, stable nuclides.Ī nuclide is described by the mass number (A) and the atomic number (Z). We describe it by the composition of its nucleus, by the number of protons, the number of neutrons, and the energy content. In simple words, nuclide is a species of atom/nucleus. It is characterized by a number of protons and neutrons. It is one of the nuclear species.Ī nuclide is like an atom or nucleus but it differs from these two. The term nuclide or nuclide is taken from the word nucleus. The word “Nuclide'' was coined by an American Chemist named Truman P.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
